Friday, 10 December 2010
Thursday, 9 December 2010
Piston
Monday, 6 December 2010
Thursday, 2 December 2010
Robot Servo Motors

The RBM-606MG features:
• Model: RBM-606MG
• Product Code: MT-010
• Made with full metal gear
• Double bearing structure at output axle
• 180 degree rotation
• Nut inserted structure (frame fixing by fastening bolt)
• White (signal), Red (+), Black (Gnd)
• Suitable for multi-joint robots
Specifications:
Torque: 7.8 kg/cm (6.0V)
9.8 kg/cm (7.0)
Power: 5V – 7.4V
Speed: 0.2 sec/60 degrees (6.0V)
0.17 sec/60 degrees (7.0V)
Dimensions: 5cm x 4cm x 2cm thick
Weight: 50g
Quantity required: 5
Denso Robot Arm
If only we had the expertise, time and money of Denso =] then this is the kind of robotic arm we would be looking to use on our strawberry picker.
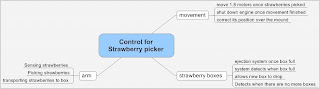
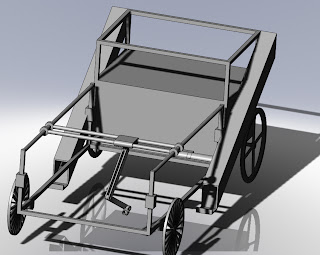
Strawberry Picker Robot Arm
The rest of the arm will be constructed from 3mm thick aluminium alloy sheet.

Project Managment
If you all agree we can discuss this in the next meeting.
Discussion-Modifications
Instead of using 4 DC motors in wheel Hub.
I would like to suggest only 2 motors on the rear hubs.
In the front wheel i would suggest a turning actuation system(Discuss the next the meeting).
DC Motor System
DC Motor
Retro-reflective sensor

For a retro-reflective application, the transmitter and
receiver are incorporated into a single housing. A reflector is mounted
opposite to the sensor and returns transmitted light back to the receiver.
Compared to a thru-beam application, retro-reflective sensors are used for
medium range or average excess gain applications. “Light-operate” sensors
provide a signal when the beam is not interrupted(target not present).
Wednesday, 1 December 2010
Vision Sensor
BVS000J
CatalogProduct yes
Switching output
Supply voltage min-21.6 V
Supply voltage max-26.4 V
Parameterization via PC
Inputs
1× Trigger, 1 x Select
58 mmX52 mmX40 mm
Ambient temperature max=+55 °C
Ambient temperature min=-10 °C
 SRH500P rotary sensor operates from either a 5Vdc regulated or 9-30Vdc unregulated supply and can be factory programmed to have a measurement range from 20° up to 360° in 1° increments. The sensor can be supplied with single output (SRH501P) or dual output (SRH502P). Both outputs are individually configurable at the factory for analogue or digital output and clockwise or anti-clockwise output.
SRH500P rotary sensor operates from either a 5Vdc regulated or 9-30Vdc unregulated supply and can be factory programmed to have a measurement range from 20° up to 360° in 1° increments. The sensor can be supplied with single output (SRH501P) or dual output (SRH502P). Both outputs are individually configurable at the factory for analogue or digital output and clockwise or anti-clockwise output.The SRH500P incorporates a 12bit non-contact Hall effect sensor with microprocessor control - offering 0.025% resolution over the selected measuring range.
Key Features
· Contactless - Hall effect technology
· Single or dual redundant output
· Analog or Digital (PWM) output
· Measurement range 20° to 360°
· 12 bit resolution
· CW or ACW output
· Less than 1mVrms output noise
· Rugged housing design, in marine grade aluminium
· Superior shaft strength
· Sealing option to IP69K
· M12 connector option for easy installation
· World leading availability

Tuesday, 30 November 2010
Friday, 26 November 2010
Tuesday, 23 November 2010
Basic System Design
 The inputs too the System will be:
The inputs too the System will be:- Light gate for strawberry row detection
- Strain Gauge for Strawberry Box weight
- Image Detector for Strawberry detection
- 5 rotational position potentiometers for arm feedback
- 4 DC Motors for drive
- 2 Stepper Motors for arm postition
- 2 Pistons for pushing out strawberry boxes when full
- Motors involved in Arm control
- one motor to opperate the scisor system on head
Friday, 19 November 2010
Tuesday, 16 November 2010
Friday, 12 November 2010
Strawberry Research
Strawberry cultivars vary remarkably in size, colour, flavor, shape, degree of fertility, season of ripening, liability to disease and constitution of plant. Some vary in foliage, and some vary materially in the relative development of their sexual organs. In most cases the flowers appear hermaphroditic in structure, but function as either male or female.
For purposes of commercial production, plants are propagated from runners and, in general, distributed as either bare root plants or plugs. Cultivation follows one of two general models, annual plasticulture or a perennial system of matted rows or mounds. A small amount of strawberries are also produced in greenhouses during the off season.
he bulk of modern commercial production uses the plasticulture system. In this method, raised beds are formed each year, fumigated, and covered with plastic to prevent weed growth and erosion. Plants, usually obtained from northern nurseries, are planted through holes punched in this covering, and irrigation tubing is run underneath. Runners are removed from the plants as they appear, to encourage the plants to put most of their energy into fruit development. At the end of the harvest season, the plastic is removed and the plants are plowed into the ground. Because strawberry plants more than a year or two old begin to decline in productivity and fruit quality, this system of replacing the plants each year allows for improved yields and denser plantings. However, because it requires a longer growing season to allow for establishment of the plants each year, and because of the increased costs in terms of forming and covering the mounds and purchasing plants each year, it is not always practical in all areas.
The other major method, which uses the same plants from year to year growing in rows or on mounds, is most common in colder climates. It has lower investment costs, and lower overall maintenance requirements.Yields are typically lower than in plasticulture.
A third method uses a compost sock. Plants grown in compost socks have been shown to produce significantly higher oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC), flavonoids, anthocyanins, fructose, glucose, sucrose, malic acid, and citric acid than fruit produced in the black plastic mulch or matted row systems. Similar results in an earlier 2003 study conducted by the US Dept of Agriculture, at the Agricultural Research Service, in Beltsville Maryland, confirms how compost plays a role in the bioactive qualities of two strawberry cultivars.
Strawberries are often grouped according to their flowering habit. Traditionally, this has consisted of a division between "June-bearing" strawberries, which bear their fruit in the early summer and "ever-bearing" strawberries, which often bear several crops of fruit throughout the season. Research has shown recently that strawberries actually occur in three basic flowering habits: short-day, long-day, and day-neutral. These refer to the day-length sensitivity of the plant and the type of photoperiod that induces flower formation. Day-neutral cultivars produce flowers regardless of the photoperiod.
Strawberries may also be propagated by seed, though this is primarily a hobby activity, and is not widely practiced commercially. A few seed-propagated cultivars have been developed for home use, and research into growing from seed commercially is ongoing. Seeds are acquired either via commercial seed suppliers, or by collecting and saving them from the fruit.
Strawberries can also be grown indoors in strawberry pots.
Most strawberry plants are now fed with artificial fertilizers, both before and after harvesting, and often before planting in plasticulture.
The harvesting and cleaning process has not changed substantially over time. The delicate strawberries are still harvested by hand. Grading and packing often occurs in the field, rather than in a processing facility. In large operations, strawberries are cleaned by means of water streams and shaking conveyor belts.
Thursday, 11 November 2010
Minutes of First Meeting
Project strawberry picking device
Ideas from meeting
• A buggy device that travels done the rows of the strawberry field using mountain bike wheels on either side of a strawberry mount in the channel
• A sensor rack (preliminary name) in front that hold a mix of colour sensors and also a lights that will map a matrix and recognise where the strawberry are in a confined area. It is also able to penetrate the vegetation in order to locate the strawberrys.
• Followed by a series of arms that will be picking up the strawberry depending if they are ripe or not.
• These arms will be holding sensors that will recognise if the fruit is ripe or not. (colour sensors)
Robotic arm
sensor
• They was an idea that the device could have a pressure or weight sensor in the container where it will notify us when the container is full prompting us to change or empty it.
(these are a brief summary of all the points we discussed )
Roles
James –
integration/ manager
Integrating the system
(helping everybody else out)
Tababi –
sensors
On arms front rack
Calibration of sensors
Price of sensors ETC
Adryan -
control developing the system
The sensors and actuator ETCs
Assan –
actuation and control
Looking at the motors and servos.
Ilute –
Actuation / Control
Action swe agreed on before next meeting.
• We would all go away and look at strawberry picking so we have a better idea of what goes into the process before next meeting